FaceSwap: Target이미지의 facial expressions, head pose, and backgrounds를 유지한채 Source 이미지의 persion-identity를 바꾸는 작업
Table of contents
- Abstract
- Introduction
- Problem Formulation
- Challenges
- Method
- Experiments
- Evaluation Details
- Conclusion
Abstract
- FaceSwap을 수행하기 위해 기존 방법론들의 경우 complex architectures와 loss functions을 설계하는 방식으로 디자인되어옴
- 이러한 방식은 다양한 hyperparameter tuning이 요구되어 학습을 성공시키기까지 많은 수작업이 동반됨
- 본 논문에서는 일일이 모델을 튜닝하는 방식 대신, 더욱 강건한 identity network(focus smoothness of the identity embedding)를 학습시켜 안정적인 face변환이 가능한
Smooth-Swap방법론을 제안함
- FaceSwap을 어렵게 만드는 요인들(Assumption about difficulty of face-swapping)
- non-smooth한 embedding space에서는 gradient가 unstable하게 optimize됨
- 본 논문에서는 identity embedder를
supervised contrastive learning방식으로 학습시켜 embedding space를 smooth하게 개선시킴 - 비교 실험을 통해 smooth embedder가 더 빠르고 안정적이게 학습을 수렴시키고 가장 기본적인 아키텍쳐만으로도(simple U-Net based generator and three basic loss function) 기존 방법론보다 성능의 우위를 가지는 것을 보임
Introduction
- FaceSwap시 faithful한 identity swapping을 위해선 얼굴의 shape을 변화시키는 것이 중요함
- 하지만 label(Swapped images)이 없는 Unsupervised Setting에서 guidance없이 pixel에 큰 변화를 주는 것은 어려운 일
- 이를 해결하기 위해 기존 방법론들의 경우, segmentation(mask-based mixing)이나 3DMM(3D face-shape modeling)과 같은 component를 추가하는 방식을 채택
- 이러한 방식은 face shape를 효과적으로 변화시키고 swapped 이미지의 퀄리티를 높일 수 있으나
- hyperparameter와 loss function에 의한 complexity가 증가하여 성공적인 학습이 더 어려워지는 문제가 있음
- 본 연구에서는, 개선된 smoothness를 가진 새로운 embedding model을 제안하여 외부 component를 의존하지 않고 효과적으로 대처할 수 있는 face-swapping 방법론을 제안함
Contribution
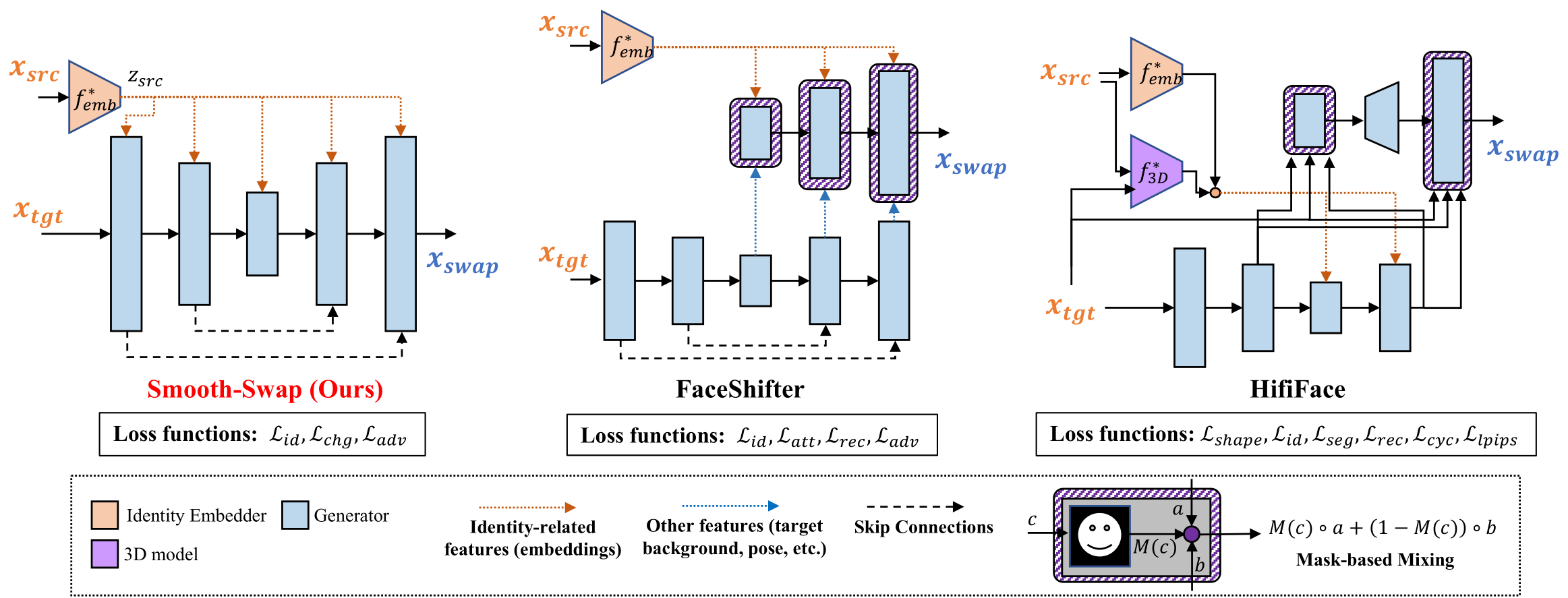
Simple architecture
simple U-Net based generator, which does not involve any handcrafted components as the existing models
Simple loss function
using minimal loss(identity, pixel-level change, adv) function for face-swapping
Fast training
smooth identity embedder allows faster training of the generator by providing more stable gradient information
Problem Formulation
C1. Swapped된 이미지는 Source image의 identity를 가지고있어야한다
- $L(x_{swap}, x_{src})$
C2. Swapped된 이미지는 target image의 expression, pose and background를 유지해야한다
-
$L(x_{swap}, x_{tgt})$
- faceSwap 모델 학습의 어려움은 C1과 C2 사이의 상충관계로부터 비롯됨
- C1을 강조하면 C2가 약해지고, C2를 강조하면 C1이 약해진다
- ($x_{swap}$과 $x_{tgt}$)간 loss를 걸어주며 ($x_{swap}$과 $x_{src}$)간 perceptual or pixel level loss를 걸어주어 Source의 특징을 반영하도록 함
Challenges
3.1 Challenges for Changing Identity
- 위와 같은 loss를 통해 Source 이미지와 Target 이미지의 절충된 합성 이미지를 얻을 수 있음
- 사람을 identify하기 위해선 swapped face의 shape이 source shape에 맞게 적절히 바뀔 필요성이 있음
- 하지만 loss를 이용한 방법만으론 face shape(geometric transformation)을 변화시키기에 충분하지 않은 부분이 있음
- 기존 방법론(HifiFace)의 경우, face shape을 바꾸는데 3D Model을 활용하여 shape 정보를 포착하고 활용
- 본 논문에서는 추가적인 모델이나 데이터 없이 Identity Embedding Space를 견고하게 만드는 것만으로 face shape에 대한 변화를 더 잘 일으키는 것을 말하고 있음
3.2 Importance of A Smooth Identity Embedder (vs ArcFace)
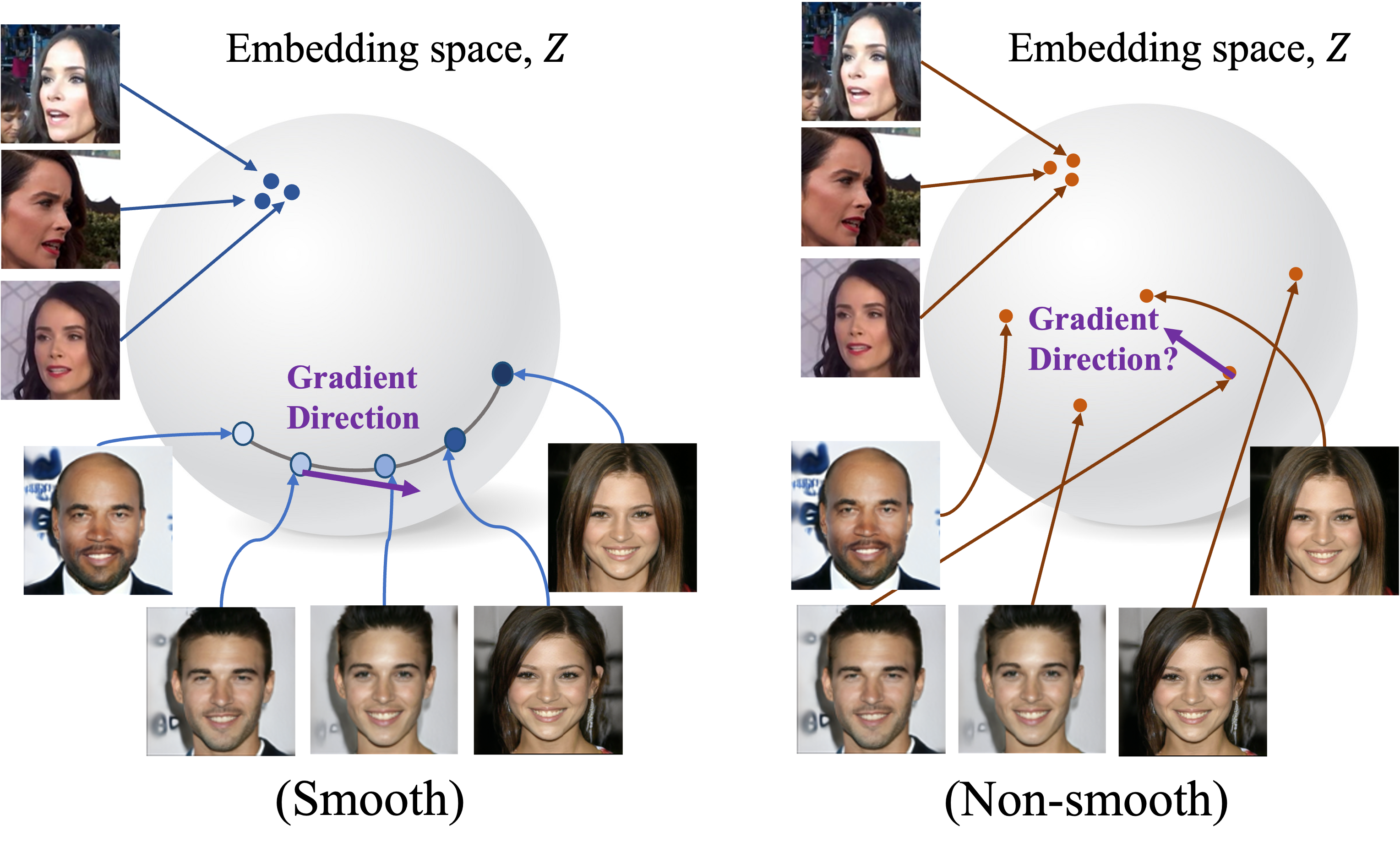
- 대부분의 face swapping 모델들은 Arc-Face를 identity embedder로 활용하고 있음
- 얼굴 이미지의 identitiy 유사도를 측정해주는 매트릭
- 하지만 기존 Arc-Face의 경우, 학습시 classification(discriminative한 task)을 기반으로 학습하기 때문에 embedding space가 매우 non-smooth하다는 단점이 있음
- Arc-Face의경우, 사람들간의 차이가 크게 나는 특징을 위주로 학습하기 때문에 동일인물에 대한 변화(나이가 젊은, 나이든), (살이찐 , 다이어트한)에 대해선 구분하기 어려움
- Smooth는 Contrastive loss를 통해 identity정보를 최대화하려는 방향으로 학습함으로써
- positive sample을 비슷한 곳에 negative sample은 멀리 embedding
- 이러한 풍부한 특징을 고려하여 구분할 수 있게끔 학습함
- $x_{swap}$을 생성해낼 때, gradient가 일관되고 정확해야 좋은 품질의 swapped 이미지를 얻을 수 있음
- gradient는 generator가 이미지를 잘못합성하였을 때, 어떻게 수정되어야하는지 feedback을 줌
- 모델이 identity vector에 따라 상반된 C1, C2 loss를 optimize하는데 합성된 이미지들이 급격히 변하면 최적의 합성 결과를 유도하기 어려움(loss surface가 불안정)
- non-smooth Embedding space의 경우, gradient direction이 noisy함
- smooth embedder의 경우 $x_{tgt}$의 identity를 변화시킬 때, 조금 더 smooth한 경로로 좋은 gradient direction을 제공
- the ArcFace embedder보다 빠르고 안정적이게 학습을 돕는 것을 보임
Method
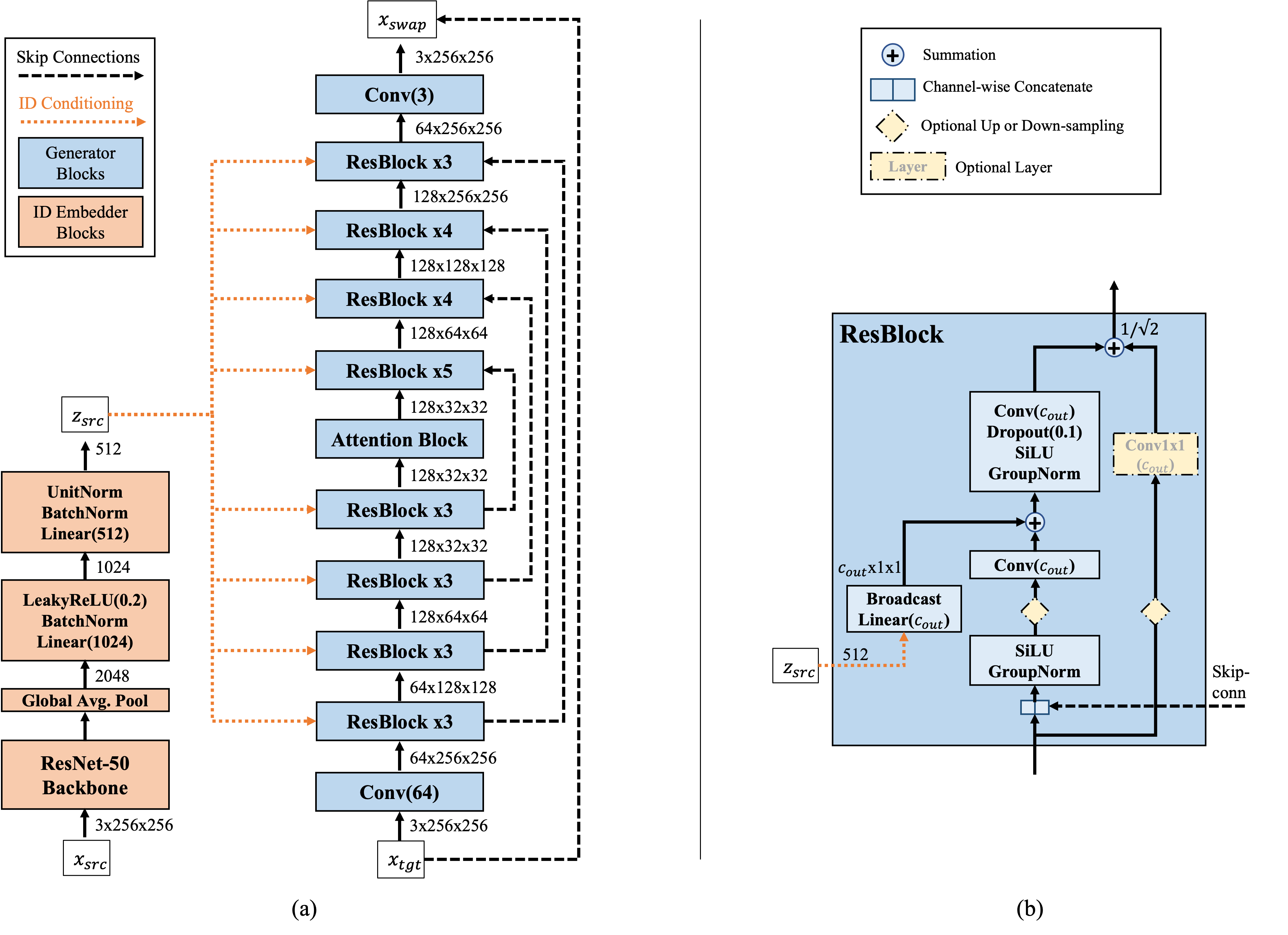
4.1 Smooth Identity Embedder
- ResNet50을 backbone으로 사용
- smooth identity embedder를 학습하기 위해,
supervised contrastive learning loss를 활용
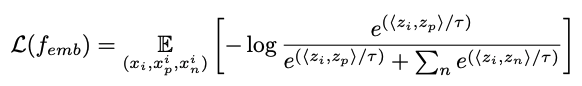
- $x_i$: sample from the training dataset
- $x_p^i$: positive samples(images having the same identity as $x_i$)
- $x_n^i$: negative samples(having a different identity)
4.2 Generator Architecture
NCSN++(score-based generative modeling) 모델의 아키텍쳐 사용- 기존 U-Net 구조에 noise를 conditional하게 넣어주는 구조
- time embedding vector를 identity embedding vector로 대체함
- noise를 identity vector로 대체하여 forward process동안 점진적으로 입혀냄
- 기존 U-Net 구조에 noise를 conditional하게 넣어주는 구조
4.3 Discriminator
- StyleGAN2
4.4 Loss Functions
- we use three most basic loss functions
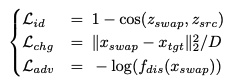
- $L_{chg}$: simpler pixel-level change loss instead of the feature-level loss
- D: stands for the number of dimensions of X(training data)
Experiments
5.1 Datasets
- Identity embedder
- VGGFace2 dataset, which contains 3.3M identity-labeled images of 9k subjects.
- We crop and align VGGFace2 images using the same procedure as FFHQ.
- Generator
- FFHQ dataset, which contains 70k aligned face images.
- We use the 10% of images for testing.
Evaluation Details
6.1 Quantitative Evaluations
대부분 FaceSwap 모델의 경우 public code를 공개하지 않아 FaceForensic++(FF++) datasets에 생성된 이미지를 활용하여 Evaluation을 진행
- Evaluate various metric
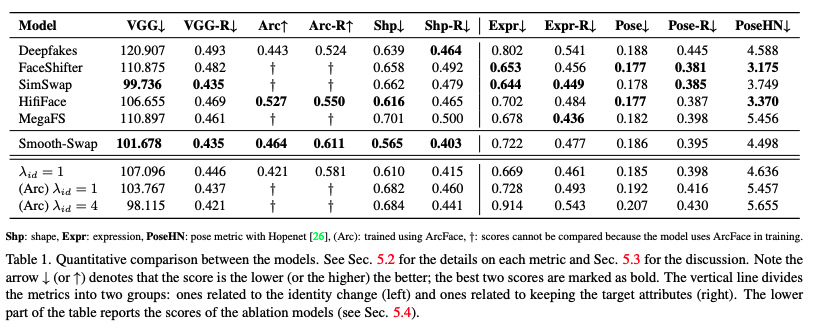
- identity ($x_{swap}$→$x_{src}$)
- VGGFace2과 ArcFace embedder를 활용하여 $x_{swap}$과 $x_{src}$간 embedding distance와 cosine similarity 계산
- shape ($x_{swap}$→$x_{src}$)
- 3D face model의 파라미터를 측정하여 L2 distance를 계산
- expression ($x_{swap}$→$x_{tgt}$)
- 3D face model의 파라미터를 측정하여 L2 distance를 계산
- pose ($x_{swap}$→$x_{tgt}$)
- 3D face model의 파라미터를 측정하여 L2 distance를 계산
- Smooth-Swap의 경우 identity scores (VGG, Arc, and Shp)에서 높은 퍼포먼스를 기록한 반면 expression과 pose에서는 조금 떨어지는 수치를 보임
- λid를 떨어뜨리면 expression score가 오르긴 하였으나 identity를 유지하는게 중요하기 때문에 높게 고정시킴
6.2 Basic Face-Swapping Performance
FaceForensics++ dataset에서 swap된 결과물을 획득하여 모델간 비교 진행
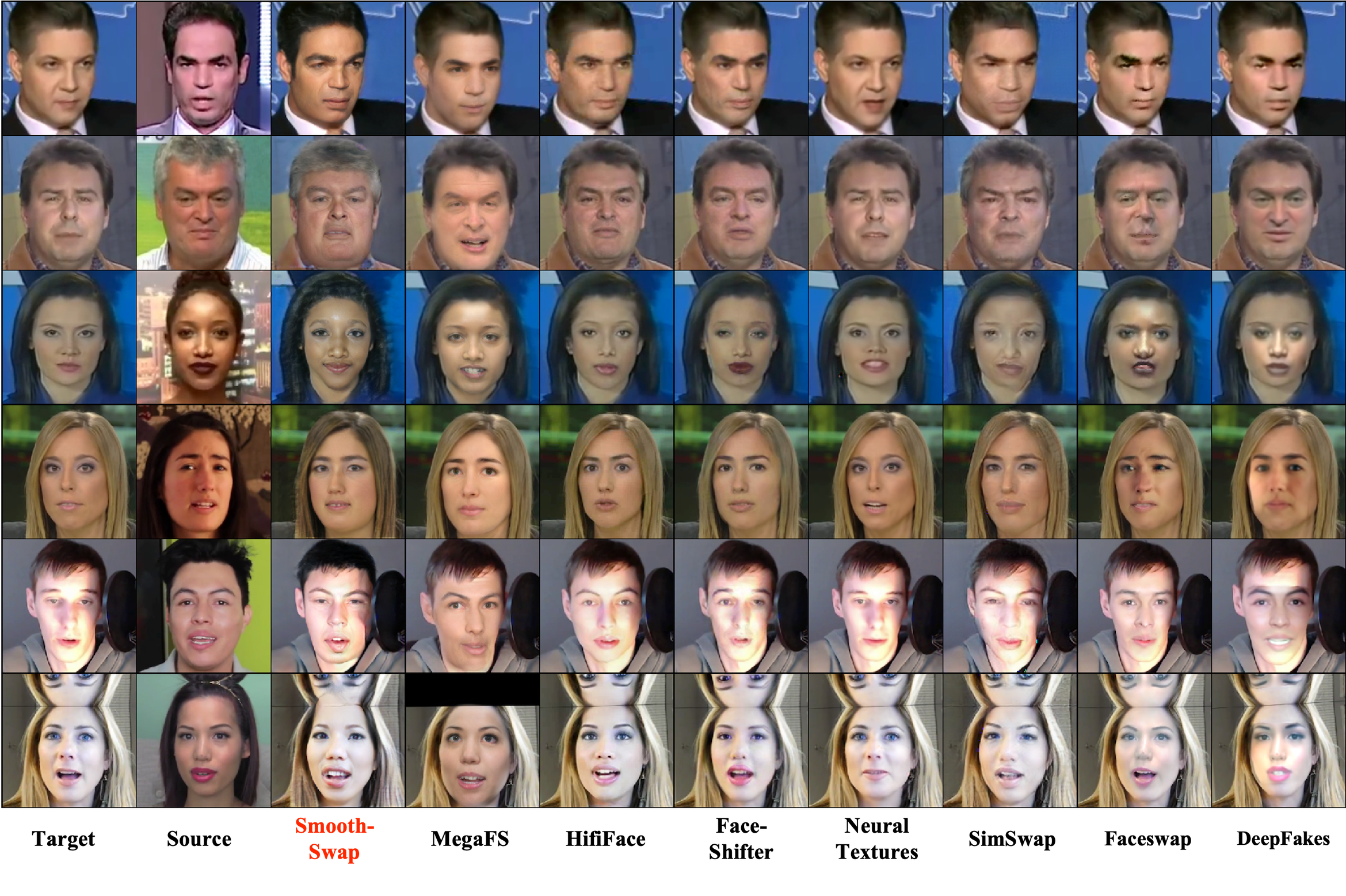

- 다른 모델의 경우, 대부분 texture를 입혀내는 것에 한정된 반면, Smooth-Swap의 경우 face shape를 더욱 유연하게 변화시킴(2행: 둥글게, 5행: 얇게)
- Skin thones, hair colors와 같은 identity attributes도 source에 가깝게 더 잘 matching 시킴
6.3 Ablation Study on the Identity Embedder
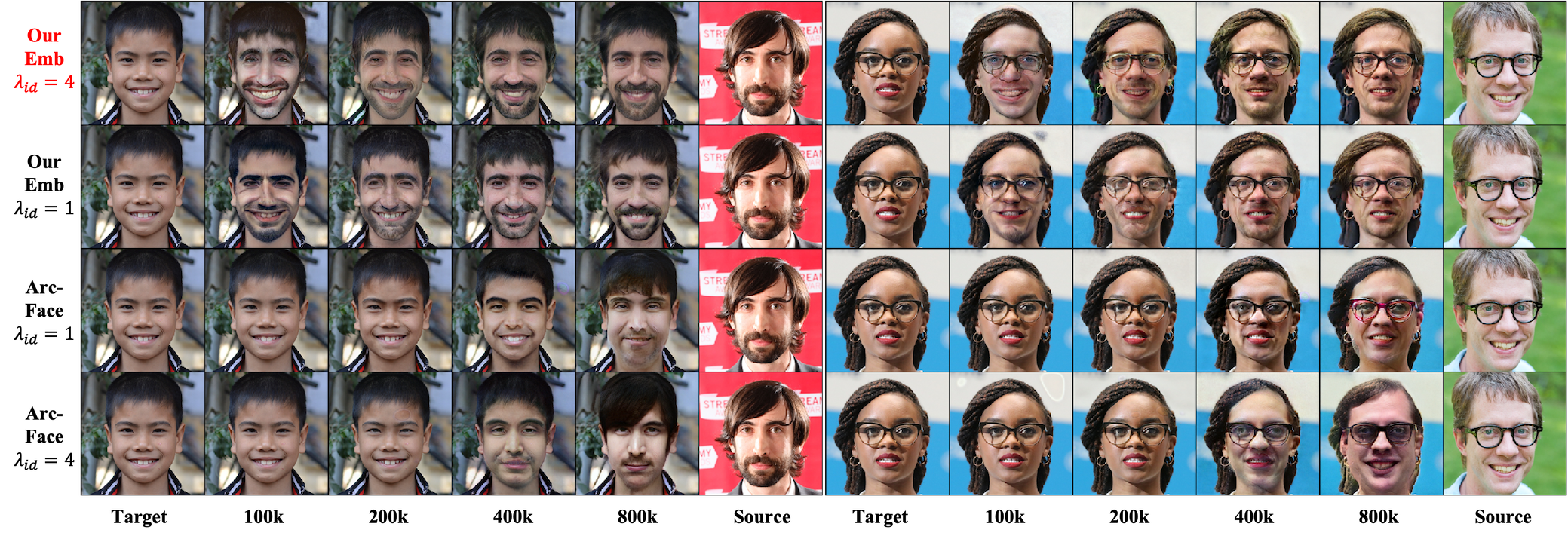

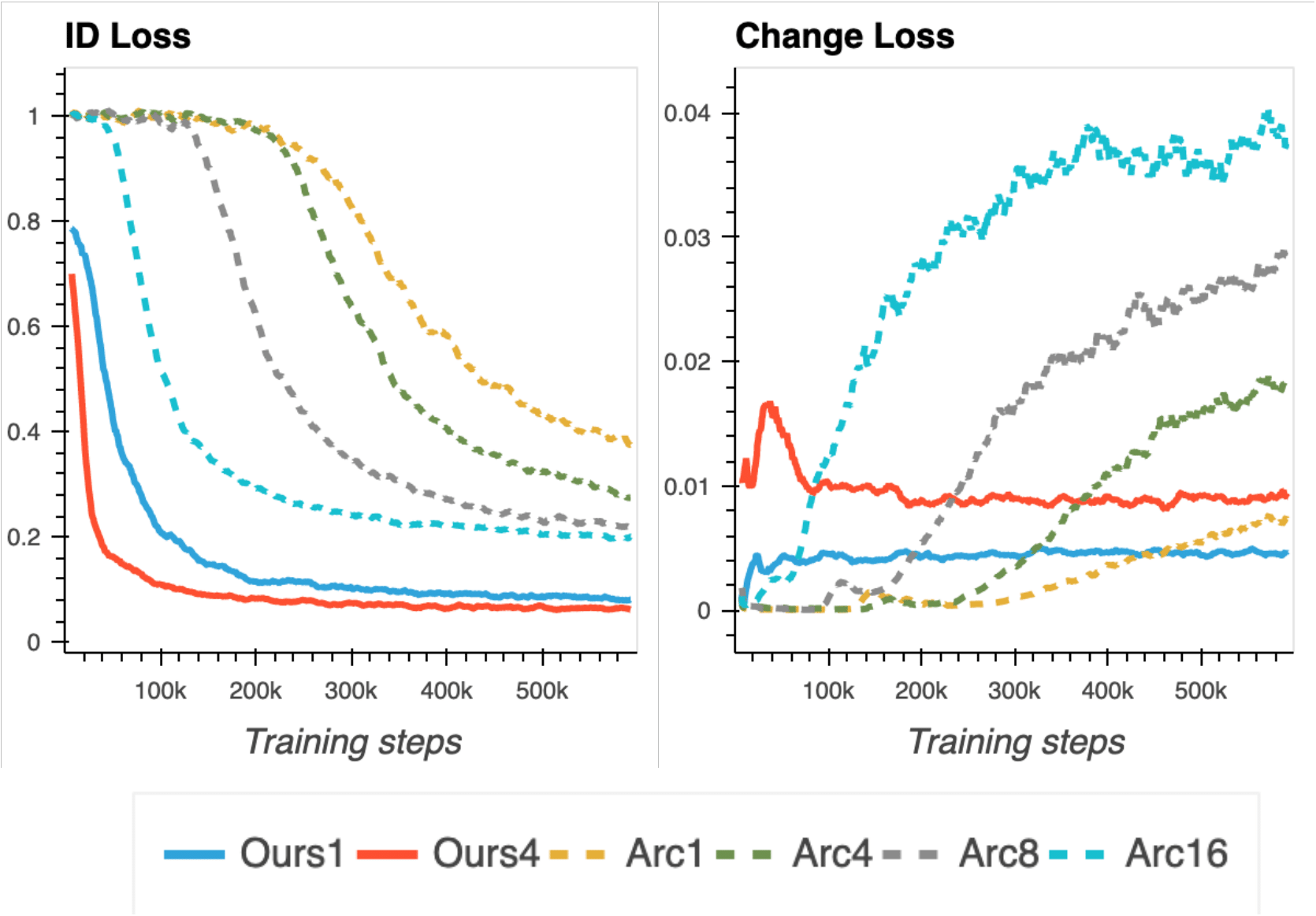
- Smooth Embedder가 Arc-Face에 비해 더 빠르고 안정적으로 학습됨
- Fig.7의 왼쪽 그래프의 경우, Smooth Swap모델이 Arc-Face에 비해 더 낮은 값으로 빠르게 수렴
- Arc-Face의 경우, λid를 16으로 키웠을 때 identity loss가 낮아졌으나 change loss에서 급격하게 향상됨
6.4 Identity Embedding Performance
- Identity embedder와 다른 baseline embedder간의 성능 비교
-
embedding space가 smooth할수록 $d_{smooth}$ 값은 작아짐
-
수식
-
$x_a$, $x_b$: ffhq from testset / $x_c$: ffhq from trainset (학습 sample이 많기 때문에 trainset이용)
$z_C = f_{emb}(x_C)$ $x_C = argmin_{x \in train} \parallel Slerp-f_{emb}(x) \parallel$ -
smooth swap의 경우, identity 정보를 최대화 시키는 방향으로 학습을 하기 때문에 embedding space가 조금 더 continuous하게 형성됨 → 다채로운 identity 표현이 가능
-
반면 non-smooth의 경우, interpolation시 이미지가 잘 변화하지 않아 $z_C$와 가까운 이미지를 만드는데 있어 더 어려움이 있음
-
따라서 smooth의 경우 분자를 더 작게 좁힐 수 있는 가능성을 더 많이 내포하고 있음
- Smooth-Swap의 경우, ArcFace와 VGGFace2에 비해 더 높은 smoothness를 보임
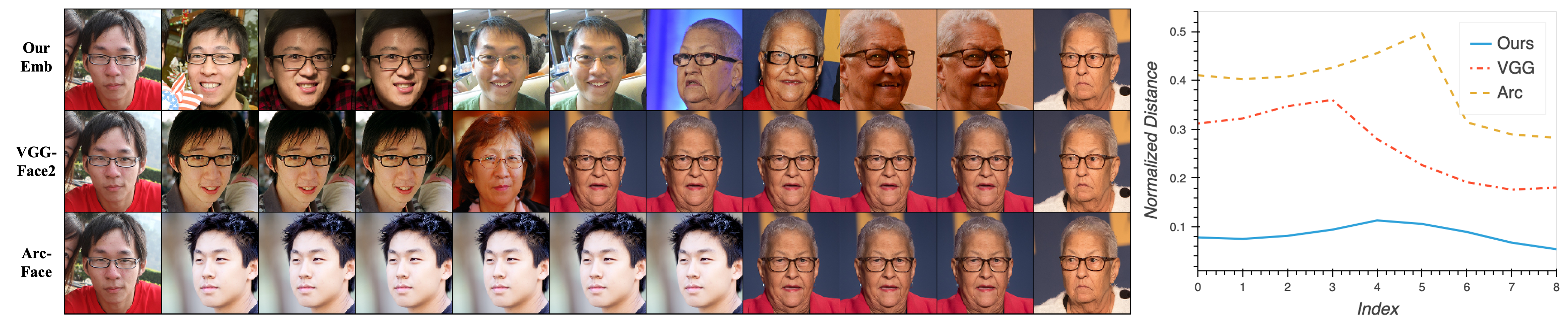

- Fig. 9. Sample $x_a$와 $x_b$를 interpolating 했을 때 결과 이미지(r ∈ [0.1, · · · , 0.9])
- VGG-Face2와 ArcFace의 경우, 동일한 identity가 반복적으로 나타나지만 smooth-swap의 경우, interpolation함에 따라 결과이미지가 천천히 변화
- interpolation시 새롭게 나타난 이미지 수를 카운팅하여 score를 측정
- Smooth-Swap: 5.13±1.18 / VGGFace2: 4.42±1.41 / ArcFAce: 4.25±1.33
Conclusion
- 많은 기존 모델의 경우 여러가지 외부 component를 handling 해야하는 이슈가 있었음
- smooth swap은 smooth identity embedder를 통해 간단한 generator와 loss만으로이 학습가능함을 보임
- identity metrics에서 우수한 성능을 보이는 smooth swap을 통해, 모델이 더 안정적이고 빠르게 학습하도록 기여
- face shape에서 유연한 변화를 보였으나 target이미지의 pose와 expression 유지가 떨어지는 문제가 있었음
개선할 부분
- FaceSwap 계열에서 Shape deformation이 source identity를 확인하는데 중요한 요소라면 AdaLIN(Adaptive Layer-Instance Normalization)의 도입이 효과적일 것을 기대
- 1d identity vector를 AdaIN으로 바로 넘겨주는 것이 아닌 2d identity Map으로 projection시켜 합성시키는 방안
- StyleMapGAN 아이디어: spatial한 정보를 고려한 identity map의 경우 보다 정확한 최적화 연산과 지역별 합성이 가능